UBlox EVK-M8N GPS
This tutorial will guide you through the process of connecting a UBlox GPS module to your Leo Rover.
EVK-7 / EVK-8 / EVK-M8 evaluation kits make evaluating the high performance u-blox 7, u-blox 8 and u-blox M8 positioning products simple. The built-in USB interface provides both power supply and high-speed data transfer, and eliminates the need for an external power supply. The u-blox evaluation kits are compact, and their user-friendly interface and power supply make them ideally suited for use in laboratories, vehicles and outdoor locations.
In this tutorial we will present the process of connecting a UBlox GPS module to your Leo Rover and integrating it with the system on the UBlox EVK-M8N GPS module example.
The steps might slightly differ for other UBlox models, but should be essentially similar.
What to expect?
After completing this tutorial, you should be able to gather the GPS data and get it published on ROS topics.
Prerequisites
Referenced products
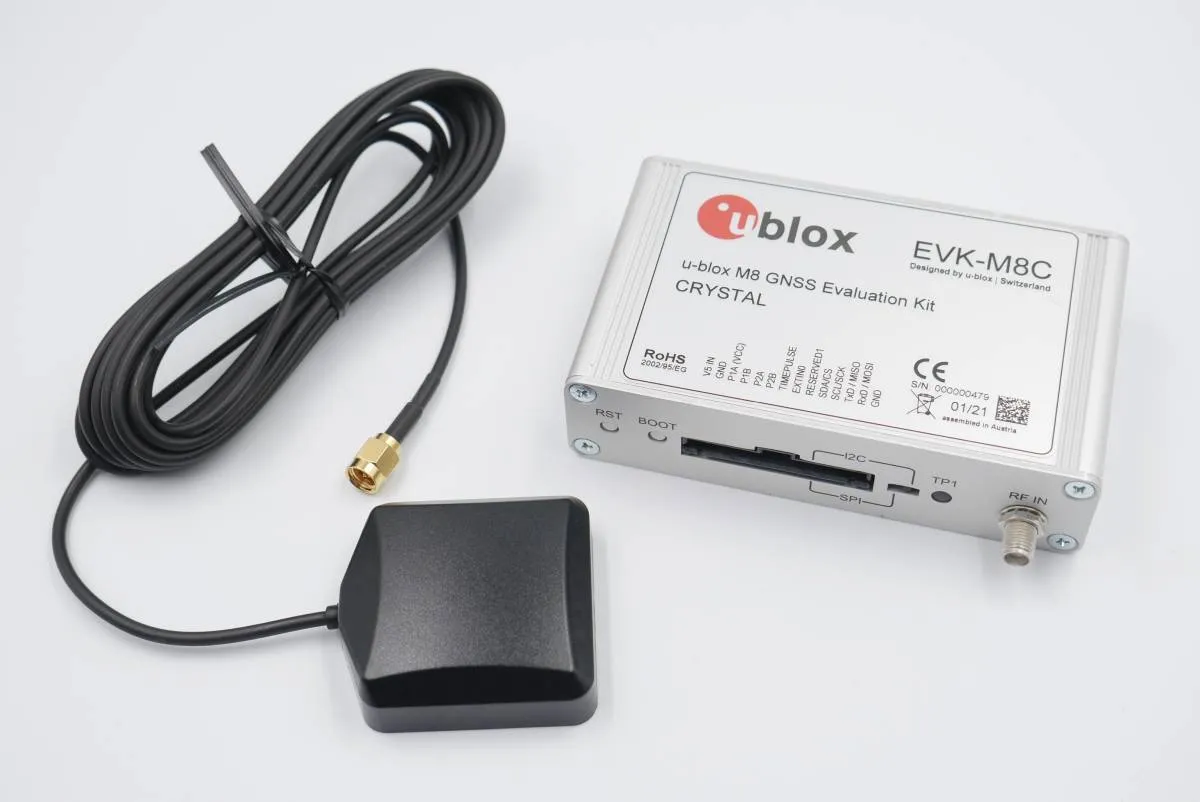

List of components
- UBlox GPS module (we have used the UBlox EVK-M8N GPS module)
- Any computer which you can connect to the rover via ssh.
Mechanical integration
When it comes to mounting the module, any solution that works for you is okay. You can 3D print a special mounting plate, use a velcro or even a tape.
Wiring and electronics connection
Wiring up the module is very simple, as it doesn't require external power supply. You just need to connect the module with a USB cable with the rover via the USB socket in the mounting plate. There is a micro-usb mounting hole with the USB sign on the module, and you need to plug in the USB cable there.
Software integration
The first thing you can do is to make sure your device has the correct
permissions and is available at the fixed path on your system. To do this, you
can add the following rule to the udev service. We will need idVendor and
idProduct, to make the rules for the correct device. To get that information,
you need to connect to the rover via ssh, and then, you can use the lsusb
command. It will list all connected usb devices. In the output, you should look
for something named like U-Blox AG [u-blox 8]:
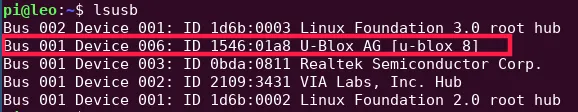
Now, our idVendor and idProduct are the two strings after "ID" divided by
colon. In our case, idVendor is 1546 and idProduct is 01a8.
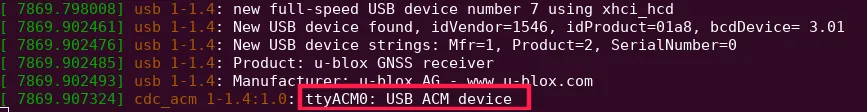
After getting those two, the only thing that is left is the port that the device connects to. You can get it by running in the terminal the command:
dmesg -w
and then connecting the module to the rover. You should see that the new device
is registered, and on what port (with this command, you can also get the
idVendor and idProduct values).
Now, you need to make a udev rules file.
KERNEL=="ttyACM*", ATTRS{idVendor}=="1546", ATTRS{idProduct}=="01a8", MODE="0666", GROUP="dialout", SYMLINK+="ublox_gps"
Paste these lines to /etc/udev/rules.d/ublox.rules file and reload udev
rules by typing:
sudo udevadm control --reload-rules && sudo udevadm trigger
Your device should now be available at the /dev/ublox_gps path.
We want the sensor functionality to be available in the ROS ecosystem, so you should install a ROS package that provides a node for the sensor you are trying to integrate.
sudo apt install ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-ublox
Now, create a launch file that would start the node with a fitting configuration.
<launch>
<node name="ublox_gps_node" pkg="ublox_gps" type="ublox_gps" clear_params="true" output="screen">
<rosparam command="load" file="$(find ublox_gps)/config/nmea.yaml"/>
<param name="device" value="/dev/ublox_gps"/>
<param name="frame_id" value="ublox_frame"/>
</node>
</launch>
Include your launch file in the robot.launch file (somewhere between
<launch> tags), so that your node will start at boot.
In /etc/ros/robot.launch:
<include file="/etc/ros/gps.launch"/>
Your robot should be aware of where the module is located and what space it occupies. You can ensure it does that by creating a URDF model of the module.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot>
<link name="ublox_frame"/>
<joint name="ublox_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="-0.05 0 0"/>
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="ublox_frame"/>
</joint>
</robot>
Make sure that "frame_id" param in the launch file and "link name" in ublox.urdf.xacro file have the same value.
And including it in the description that is uploaded at boot.
<xacro:include filename="/etc/ros/urdf/ublox.urdf.xacro"/>
The last step is to either reboot the robot
reboot
or restart the leo service
sudo systemctl restart leo
Examples
Checking the GPS module accuracy
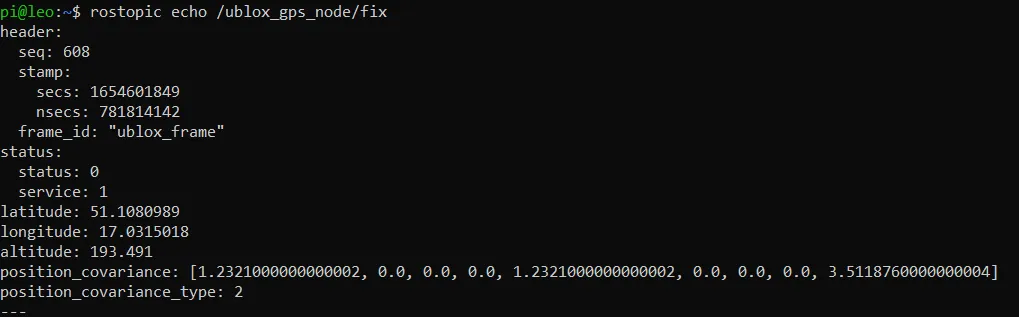
Type this command into the console to check the data sent by GPS module:
rostopic echo /ublox_gps_node/fix
You should see a lot of data flowing through the topic. Stop the data acquisition with Ctrl+C and have a look on a usual data frame.

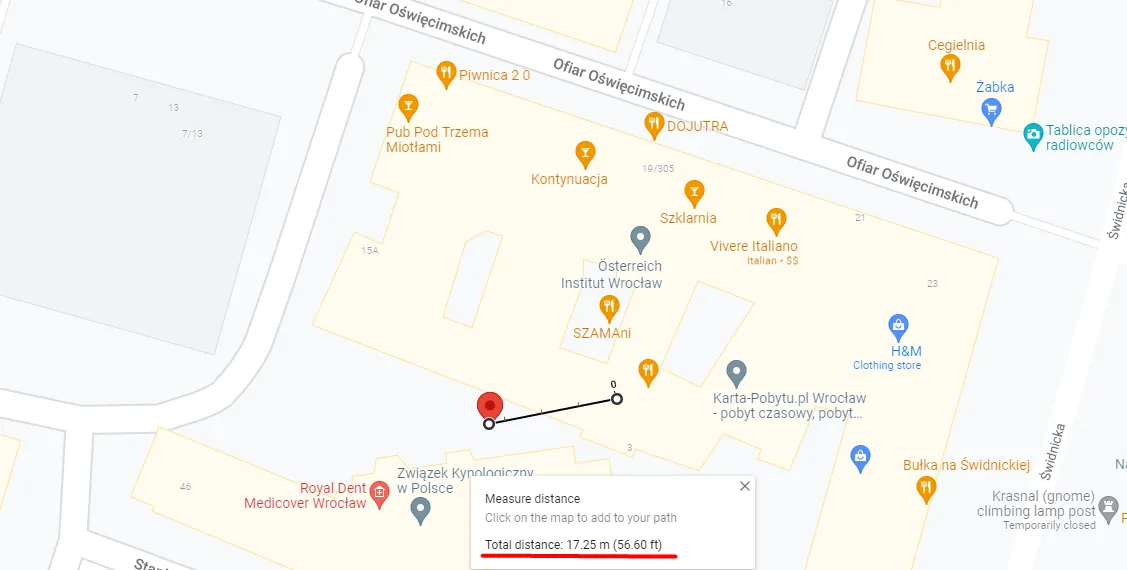
Using Google Maps you can easily evaluate the precision of your GPS module. Find the latitude and longitude data in the data frames send by the module. Copy and paste it into google maps search bar. When a pin appears, you should be able to see where the module thinks it is.
Usually accuracy is off by some factor. Depending on the amount of interferences and the quality of the GPS module, the difference between real location and the position gathered with GPS module may vary.
Right click on the map location you believe you are at and use "Measure distance" option at the bottom of the list. Then, create another spot for the distance measuring tool right where the red marker is. Google will then do the math and show you the distance between your real location and where the GPS module thinks it is.
Data visualization with Mapviz
Using Mapviz - a package similar to RViz, yet focused on visualization of 2D data - you can easily visualize the data gathered by the GPS module. Installing the package boils down to using this command:
sudo apt-get install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-mapviz ros-$ROS_DISTRO-mapviz-plugins ros-$ROS_DISTRO-tile-map ros-$ROS_DISTRO-multires-image
Since Mapviz is a program using GUI you may want to connect to the Leo Rover via remote desktop. Follow this tutorial if you want to learn how:
Launch Mapviz with:
roslaunch mapviz mapviz.launch
You'll be greeted by a blank screen with configuration window on the left. Using
the Add button on the bottom of this window add tile_map and navsat
plugins. Change the source of tile_map to Stamen (terrain) (Or any other
available option) and the topic of navsat to the topic your GPS module is
publishing data to (for us it's /ublox_gps_node/fix).
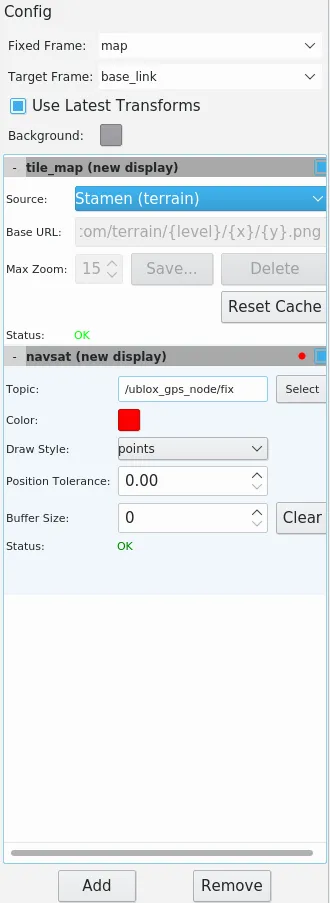
Make sure the tile_map plugin is listed first and navsat second. Otherwise, points created by navsat will be hidden behind the map tiles.
From now on, a dot will appear on the map every time your GPS module publishes data at the topic you chose.
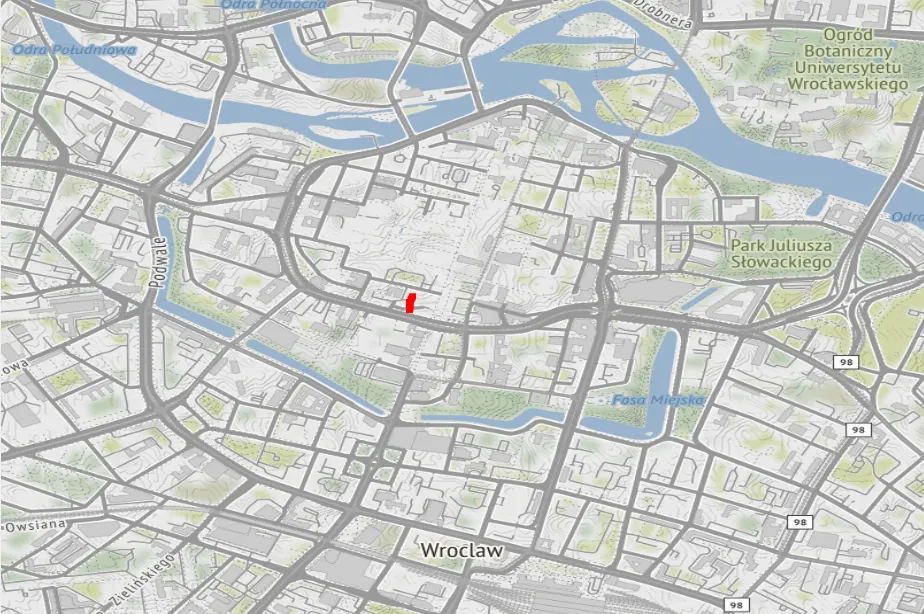
What next?
GPS modules are commonly used in projects involving outside autonomous navigation. As of right now, we have no tutorials on such a thing, however, our tutorial on indoor autonomous navigation you might be something you'll be interested in.
You can also check our Integrations page for other instructions.