Multi-Rover ROS Setup
The advanced guides are exclusively for ROS 1. We are actively working on updating these guides to also support ROS 2.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to configure many rovers in one network, so that they will see each other and will communicate.
Prerequisites
In such setup, we need every rover, to have its own robot namespace for ROS nodes and topics, and only one ROS master. We also need to connect all the rovers to the same network, and know their IP addresses.
Once all rovers are connected to the same network, we can start configuring them.
You will need to make almost the same steps on every rover. The only differences are for the rover with ROS master on it, but it will be marked, how given step is different for the main rover (the rover with ROS master).
Getting IP address
First, we need to know the IP address of the rover in the network with all other rovers. To get it, you have to connect to the rover via ssh, and type in the terminal
ip addr
This will show addresses assigned to all network interfaces, we just need to
check the correct interface. If you didn't make many changes to the network
setup before, then you need to find the wlan_int interface (if you did some
changes and don't have this interface, you need to find the interface connected
to the network). There, you can find the address next to inet tag.
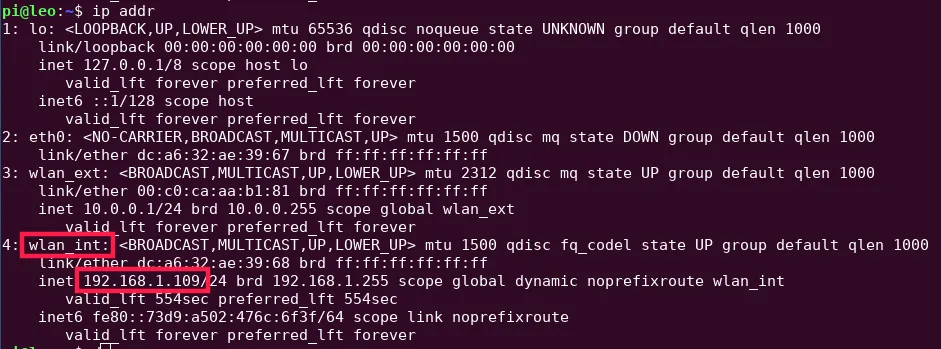
You need to remember or write somewhere this address.
You need IP address of the main rover for other rovers, so remember specially what address it has.
Changing setup file
Now, we need to configure some environment variables. We can do this by changing
the setup.bash file in the /etc/ros directory. To do so, type:
nano /etc/ros/setup.bash
Here, we need to change a few things:
- make sure the
START_ROSCOREvariable is set totrueon the main rover, and for other rovers it is set tofalse - uncomment the line with variable
ROS_NAMESPACE. You also need to provide the namespace, it can beleox, where x is a number of the rover in your setup, orleo_mainfor the main rover. We need to change it, as you can't have two nodes with the same name. Setting this variable will give your node name prefix with the namespace. - make sure the line with the
ROS_HOSTNAMEvariable is commented - uncomment the line with the
ROS_IPvariable and provide the IP address of the rover - uncomment the line with the
ROS_MASTER_URIvariable. Now, for the main rover, you need to set it tohttp://localhost:11311. For other rovers, you need to set it tohttp://<ip address of main rover>:11311
Changing urdf file
We also need to change the robot.urdf.xacro file in the /etc/ros/urdf
directory. If we don't make changes in this file, all rovers will have the same
tf frames, which will give some error readings when doing something with tf
tree. To edit it, type:
nano /etc/ros/urdf/robot.urdf.xacro
In this file, you need to provide the link_prefix variable. This way we will
have distinct tf trees for every rover, as the frames will have the prefix.
You can set it to the same value that you gave to ROS_NAMESPACE environment
variable. You can find the link_prefix variable inside xacro:leo tag.
Changing launch file
In the previous paragraph, we were making changes required for working tf
tree, but those changes were not enough. We also need to change the
robot.launch file in /etc/ros directory, to make it work correctly. To
edit it, type:
nano /etc/ros/robot.launch
In this file, we include another launch file. The included launch file has ros
argument tf_frame_prefix, so we can set it here in the <include> tag, to our
value. To add it, you need to include this line in the file:
<arg name="tf_frame_prefix" value="leo_main/"/>
Your robot.launch file in the end should look like this:
<launch>
<param name="robot_description"
command="xacro /etc/ros/urdf/robot.urdf.xacro"/>
<include file="$(find leo_bringup)/launch/leo_bringup.launch">
<arg name="upload_description" value="false"/>
<arg name="tf_frame_prefix" value="leo_main/"/>
</include>
</launch>
You need to set the value of tf_frame_prefix argument in the robot.launch
file to the same value, you gave in the link_prefix variable in
robot.urdf.xacro file.